Despite its state of preservation – compromised by a long permanence in water that damaged the majority of physiognomic features – this veiled female head found in the waters of the banks of Puteoli provides us with interesting details about the activities of the nearby workshop: a neatly sheared iron joint with a square-section at the base of the neck suggests that the artefact was not a simple piece that was never assembled, but rather a damaged part of a statue that was no longer repairable.
The artefact shows a widespread pitting caused by boring sponges of the family Clionidae, present on approximately 80% of the surface. There were no other signs of visible biological degradation.
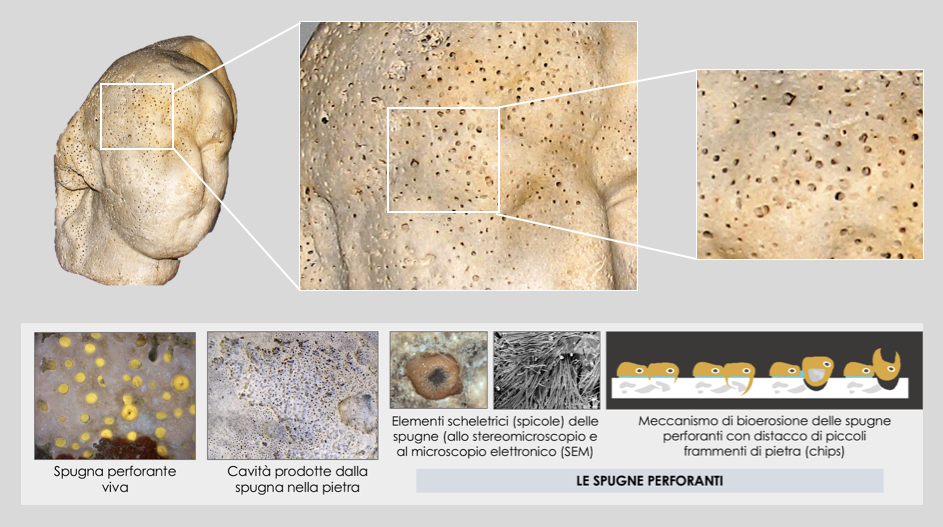
Davidde B., Ricci S., Poggi D., Bartolini M., 2010. Marine bioerosion of stone artefacts preserved in the Museo Archeologico dei Campi Flegrei in the Castle of Baia (Naples), Archaeologia Maritima Mediterranea; 7: 75-115.aDemma, F. (2010) ‘Scultori, redemptores, marmorarii ed officinae nella Puteoli romana. Fonti storiche ed archeologiche per lo studio del problema’, Mélanges de l’Ecole française de Rome. Antiquité, 122(2), pp. 399–425.
Zevi F. (cur.) 2009, Museo archeologico dei Campi Flegrei. Castello di Baia. Napoli: Electa Napoli, vol. 2, p. 56.
Demma, F. (2010) ‘Scultori, redemptores, marmorarii ed officinae nella Puteoli romana. Fonti storiche ed archeologiche per lo studio del problema’, Mélanges de l’Ecole française de Rome. Antiquité, 122(2), pp. 399–425.
Ricci S., Sacco Perasso C., Antonelli, F., Davidde Petriaggi B., 2015. Marine Bivalves colonizing roman artefacts recovered in the Gulf of Pozzuoli and in the Blue Grotto in Capri (Naples, Italy): boring and nestling species. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation (98) 89 – 100.
Ricci, S., Pietrini, A. M., Bartolini, M., Sacco Perasso, C., 2013. Role of the microboring marine organisms in the deterioration of archaeological submerged lapideous artifacts (Baia, Naples, Italy). International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation 82 (2013) 199-206.
Ricci S., Davidde B., Bartolini M., Priori G. F., 2009. Bioerosion of lapideous objects found in the underwater archaeological site of Baia (Naples). Archaeologia Maritima Mediterranea, 6: 167-188.
Zevi F. (cur.) 2009, Museo archeologico dei Campi Flegrei. Castello di Baia. Napoli: Electa Napoli, vol. 2, p. 56.



